It refers to pain in and around the ear.
This blog is to aware people that it is not mandatory that the pain in the ear occurs only when there is something wrong with the ear. It is to tell people that pain in the ear can also be caused by diseases of the head and neck.
Many COVID-19 infected patients have reported Ear congestion and Ear pain as a very upsetting symptom of the COVID-19 Omicron variant. (Reference: Internet)
This ear pain could directly be an independent symptom of the virus (studies are awaited) or most probably could be an indirect symptom of the nose and sinus congestion leading to ear involvement.
Types of EAR PAIN-
1. PRIMARY EAR PAIN:
Primary ear pain means Pain in and around the ear is can be caused by inflammatory, traumatic, and cancerous conditions of the ear.
2. SECONDARY EAR PAIN:
Secondary ear pain is a referred pain that arises from the diseases or ailments in the head and neck regions, which are innervated by the nerves that are also supplied to the ear.
CAUSES OF EAR PAIN-
PRIMARY EAR PAIN
1. ECZEMA OF OUTER EAR SKIN
SYMPTOMS –
- Scales/dryness, itching of the skin of the ear.
- Scales, dryness, itching might be present in other parts of the body also.
- In case of severe itching, the lymph nodes around the ear can be found enlarged and a little tender causing a swelling either in front or behind the ear.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1317124199-9ff17073b0ba45099a2c6e0e779d7639.jpg)

TREATMENT OF ECZEMA OF EAR-
The patient should consult a Skin specialist or a DERMATOLOGIST.
2. PERICHONDRITIS of ear:
SYMPTOMS-
- Redness, and pain in the ear.
- History of TRAUMA to the ear or RECENT PIERCING of the ear might be there.
- In severe infection, the lymph nodes around the ear can be found enlarged and a little tender causing a swelling either in front or behind the ear.
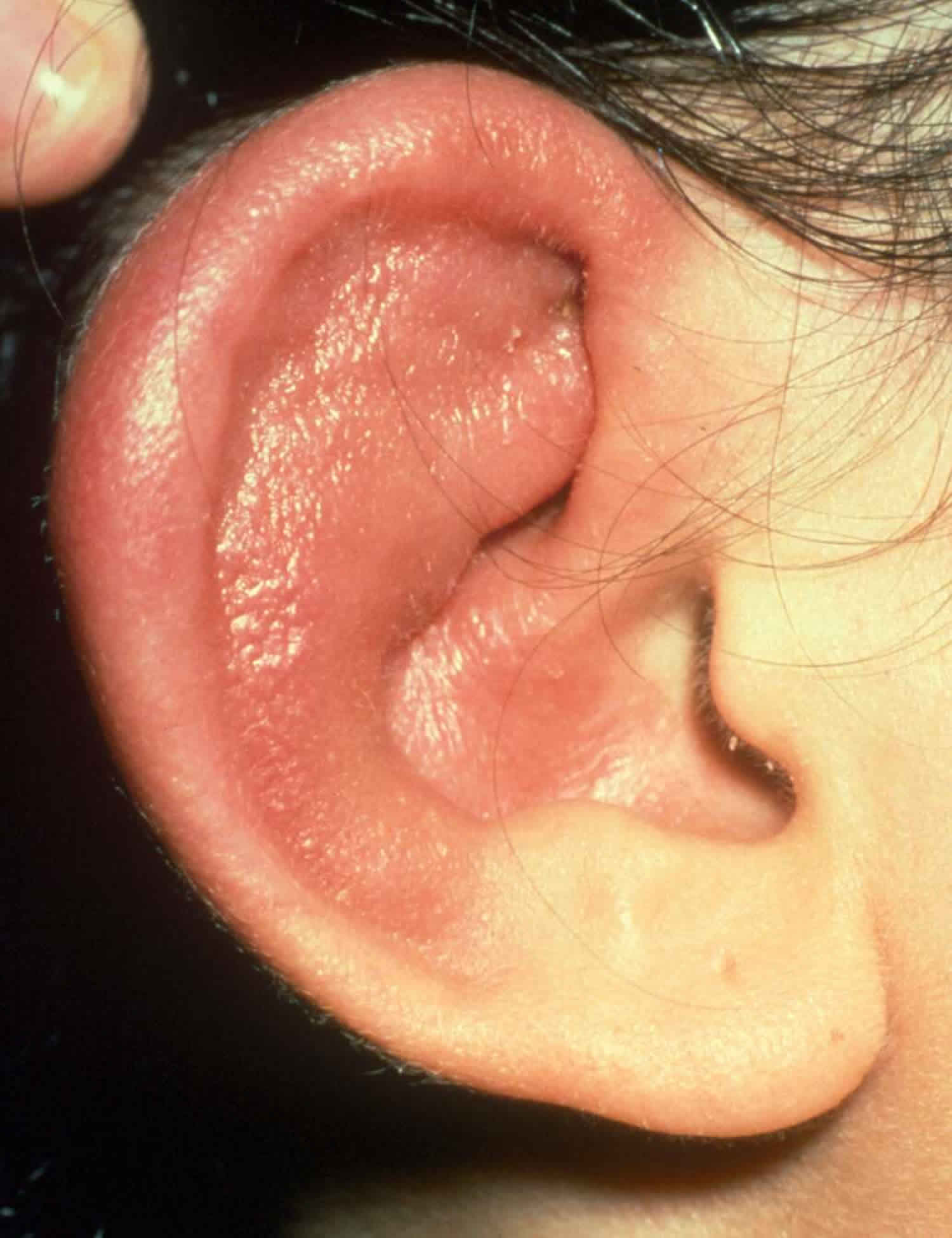
TREATMENT OF PERICHONDRITIS-
a) Intravenous ANTIBIOTICS
b) Painkillers
c) Daily Dressing
d) If Stubborn and not relieving – The patient may require Surgery where the patient may require CARTILAGE CURETTAGE.
3. SEROMA / PSEUDOCYST/HEMATOMA /ABSCESS OF EAR:
SYMPTOMS-
- Redness, pain, and swelling in the ear.
- History of TRAUMA to the ear will be there.




TREATMENT OF SEROMA / PSEUDOCYST/HEMATOMA /ABSCESS OF EAR –
a) INCISION AND DRAINAGE followed by BUTTONING OF ABSCESS/ HEMATOMA
b) Intravenous or Oral ANTIBIOTICS
c) Painkillers
d) Daily Dressing
4. FURUNCLE OR BOIL OF EAR CANAL aka OTITIS EXTERNA
SYMPTOMS-
- Excruciating pain in the ear.
- Pain aggravated on touching the ear, during chewing of food.
- Ear discharge might be there.
- Due to excessive swelling of the ear canal, the patient may experience Decreased hearing.
- In severe infection, the lymph nodes around the ear can be found enlarged and a little tender causing a swelling either in front or behind the ear.
- History of Swimming or water entering the ear during bathing may be present.
- There could be history of scratching ear using ear bud, car keys, or fingernail.

TREATMENT OF OTITIS EXTERNA-
a) Antibiotics
b) Painkillers
c) Ear drops like Candibiotic plus®, Neosporin-H® ear drops, etc.
d) Ear canal dressing with Quadriderm ointment® or Icthamol glycerine®
5. IMPACTED WAX
SYMPTOMS-
- Decreased hearing
- Pain in ear
- Ear fullness or blockage

TREATMENT OF IMPACTED WAX-
- Wax dissolving ear drops like Soliwax ® for 5-7 days, followed by Wax removal by ENT specialist using Suction, Syringing, or probe.
- DO NOT USE HYDROGEN PEROXIDE to remove the wax from the ear. The possible exothermic reaction of hydrogen peroxide can lead to severe ear skin maceration leading to severe pain and infection in ear.
6. FOREIGN BODY in ear
SYMPTOMS-
- Pain in ear
- Decreased hearing
- Something moving inside ear (in case of live insect/round foreign body)

TREATMENT –
– In case an insect has entered the ear, the following steps should be followed-
– If at home, the patient should immediately lie down with the affected ear up, and completely fill the ear canal with oil (Parachute coconut oil ®, Olive oil, Mustard oil, etc.)
– Wait for 15-20 minutes or till you feel that the insect has stopped moving.
– The patient can now turn on the other side so the affected ear is now down and wait for all the oil to come out of the ear.
– The oil can be collected in a bowl and inspected if the insect has come out of the ear with the oil or not.
– In case the foreign body is still inside the ear, Removal of the foreign body should be done by an ENT specialist using Suction, Syringing, or probe.
7. TRAUMA of Ear Canal
SYMPTOMS-
- Pain in ear
- Decreased hearing
- Ear fullness or blockage
- History of use of Ear bud, car or bike keys etc for itching of the ear canal.
- History of Assault or Accident might be there.

TREATMENT of Trauma of ear canal-
a) Keep ear dry
b) Antibiotics
c) Painkillers
d) Oral decongestants
e) If hemotympanum, the patient may require oral steroids.
8. FUNGAL INFECTION of the ear aka OTOMYCOSIS
SYMPTOMS-
- Pain in ear
- Decreased hearing
- Ear discharge, fullness/blockage

TREATMENT OF FUNGUS IN EAR-
a) Keep ear dry
b) Oral decongestants
c) Painkillers
d) Antifungal ear drops like Candid ®
e) Repeated visit to ENT doctor for ear cleaning till no fungus spore or hyphae is visible.
9. HERPES ZOSTER infection of ear (HERPES ZOSTER OTICUS or RAMSAY HUNT SYNDROME)
SYMPTOMS-
- Excruciating ear pain on one side.
- Excruciating facial pain on one side
- Vesicles (fluid filled lesions) present over the ear canal.
- Same side FACE PARALYSIS.

TREATMENT of Herpes Zoster Infection of Ear-
a) Oral ANTIVIRALS like Tab. Acyclovir 800 mg 5 times a day or Famcyclovir 500 mg TDS or Valacyclovir 1 gm TDS for 7 days.
b) Oral STEROIDS like Tab. Prednisone tapering dose 6 days course beginning usually with 1 mg/kg.
c) Topical antibiotic/steroid ear drops.
d) Eye ointment while sleeping eg. Lacrigel ®
e) Use goggles when outside the house to prevent dryness of the eyes.
f) Tape Eyelids to close eyes while sleeping.
g) Artificial tears like Refresh tears ® to keep eyes moist.
10. ACUTE OTITIS MEDIA
SYMPTOMS-
- Pain in ear
- Decreased hearing
- Ear fullness
- History of preceeding COUGH, COLD will usually be present

TREATMENT of Acute Otitis Media-
a) Intravenous or Oral Antibiotics
c) Painkillers
d) Oral decongestants
e) Ear drops like Candibiotic plus®
f) In a few cases, low-dose oral steroids can be given.
g) Patient should be advised to NOT BLOW THE NOSE HARD as it may cause a rupture of eardrum.
11. MASTOIDITIS
Chronic Otitis media with perforation or Cholesteatoma can lead to mastoiditis.
SYMPTOMS-
- Ear discharge (mucus like, blood tinged, foul smelling etc.)
- Decreased hearing
- Sensation of fullness in ears
- If complicated, can lead to Ear pain, tinnitus, vertigo, swelling in front or behind the ear.
- In advanced cases, BRAIN may get involved, leading to Meningitis, or Brain abscess(or pus)etc.


TREATMENT of Chronic Otitis Media with perforation or Cholesteatoma-
a) Intravenous or Oral Antibiotics
c) Painkillers
d) Oral decongestants
e) Ear drops like Candibiotic plus®
f) Ear Surgery is required in most cases such as Canal wall up/ Down Mastoidectomy with Tympanoplasty.
12. BAROTRAUMA
SYMPTOM-
Sudden descent and ascent in an airplane by a pilot or by a deep-sea diver in an ocean can cause the eardrum to get congested or swollen up leading to ear pain.
This most commonly occurs when the patient has a concomitant nose, sinus, or ear infection.
Very commonly seen in FREQUENT FLYERS like PILOT, CABIN CREW, or DEEP SEA DIVERS.
TREATMENT-
- AVOID FLYING OR DIVING if suffering from cough, cold, ear heaviness, ear blockage, or ear pain
- Carry Cotton plugs and plug the ear throught the air journey.
- Keep chewing a gum and keep swallowing
- Oral Antibitotics
- Oral Analgesics.
- Topical Nasal sprays
- Steam Inhalation
13. LARYNGOPHARYNGEAL REFLUX/ GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX/ HYPERACIDITY (READ MORE ABOUT LPR/GERD here)
SYMPTOMS-
– A patient who suffers from high acidity, or acid reflux as seen in cases of Laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR), or Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) where the contents of the stomach are refluxed in the throat, it is seen that this acid reflux can sometimes reach even the nasopharynx, leading to acid entering the ear through Eustachian tube opening.
– These patients complain of ear pain with burping or retching.
– Many a times, patients with Eustachian tube dysfunction can also complain of pain in ear with hiccups, or while burping or retching.
TREATMENT-
- Proton Pump Inhibitors like Sompraz®, Pantop-DSR® etc., OR
- Antacids like Gelusil®, Mucaine Gel® etc., OR
- Diet modifications.
- Avoid HOT, SPICY FOODS, CHILLIES, SMOKING, AND DRINKING.
- AVOID IMMEDIATELY LYING DOWN or SLEEPING AFTER TAKING A MEAL.
- Use GERD pillows, or BED risers.
- DO NOT take a full stomach meal at night.
SECONDARY EAR PAIN
Secondary ear pain is a referred pain that arises from the diseases or ailments in the head and neck regions, which are innervated by the nerves that are also supplied to the ear.
1. Pain carried to Ear by TRIGEMINAL NERVE.
The following diseases can carry pain to the ear via the Trigeminal nerve –
a) DENTAL DISEASES such as Caries tooth, Erupting tooth, etc.-
SYMPTOM-
- Tooth ache
- Ear ache (Referred pain)
TREATMENT-
Consult a Dentist for a tooth removal.
b) ORAL ULCERS-
SYMPTOMS-
- Ear ache (Referred pain)
- Pain or burning sensation in tongue or buccal mucosa
- Painful swallowing might be present.
- Ulcer may be visible right inside the oral cavity.
- History of trauma while brushing teeth may be present.
- History of indigestion, upset stomach may be present.
- History of SMOKING, DRINKING may be present.
TREATMENT-
- Steroid oral paste/ointment
- Local Anesthetic ointment
- If ulcer is non-healing, BIOPSY is required.
c) Infection of SALIVARY GLANDS-
SYMPTOMS-
- Ear ache (Referred pain)
- Swelling and pain of the face or near the jaw.
- Painful swallowing may be present.
- Patient may complain of sour liquid coming in the mouth intermittently.
- Swelling and redness of the floor of the mouth may be present.
TREATMENT-
- Antibiotics
- Painkillers
- Patient may be admitted in case there is excessive pain, swelling, and has difficulty in eating.
d) SCALP INFECTION leads to tender lymph nodes in front of the ear-
SYMPTOMS-
- Itching in the scalp
- Scales or Flakes in the scalp skin
TREATMENT-
- Consult a Dermatologist
e) TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT PAIN
SYMPTOMS-
- Pain in the jaw joint which is present just in front of the ear.
- Pain in ear (Referred pain)
- Painful chewing
- Patient may sometimes compalin of grinding sound from the jaw while chewing.
- Ear ache (Referred pain)
TREATMENT-
- Liquid diet
- Luke warm water mouth rinsing
- Sustained release Painkiller
- Muscle relaxant (if required)
f) Deviated nasal septum (DNS) with sharp spur or SINUSITIS
SYMPTOMS-
- Nasal obstruction
- Headache
- Nasal discharge
- Post nasal drip (PND)
- Ear pain may be a secondary complaint to nose and sinus congestion/infection due to DNS
TREATMENT-
- Nasal operation such as Septoplasty.
g) Trigeminal Neuralgia
SYMPTOM-
- Excruciating pain over one side of the face or head.
- It may invove the ear also.
TREATMENT-
Consult a Neurologist/Neurosurgeon
2. Pain carried to Ear by GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL NERVE.
The following diseases can carry pain to the ear via the Glossopharyngeal nerve –
(i) Tonsil infection aka Acute Tonsillitis.
SYMPTOMS-
- Ear ache (Referred pain)
- Itchy/Scratcy/Sore throat
- Severe pain in throat
- Painful swallowing even to saliva sometimes
- Fever
- Enlarged neck lymph nodes leading to swelling and pain near angle of jaw.
TREATMENT-
- Oral Antibiotics
- Painkillers
- Decongestants
- Betadine® gargles
(ii) Peritonsillar Abscess aka Quinsy
SYMPTOMS-
- Ear ache (Referred pain)
- Itchy/Scratcy/Sore throat
- Severe pain in throat
- Painful swallowing even to saliva sometimes
- Fever
- Enlarged neck lymph nodes leading to swelling and pain near angle of jaw.
- Hot potato voice (means The voice of the patient will be such that when a hot potato is eaten and it gets stuck to the palate)

TREATMENT-
- Intavenous or Oral Antibiotics
- Painkillers
- Decongestants
- Betadine® gargles
- Incision and Drainage of Peritonsillar abscess
(iii) Ulcer (Aphthous/ Malignant) of Soft Palate, the base of the tongue.
SYMPTOMS-
- Ear ache (Referred pain)
- Pain or burning sensation in tongue or buccal mucosa
- Painful swallowing might be present.
- Ulcer may be visible right inside the oral cavity.
- History of trauma while brushing teeth may be present.
- History of indigestion, upset stomach may be present.
- History of SMOKING, DRINKING may be present.
TREATMENT-
- Steroid oral paste/ointment
- Local Anesthetic ointment
- Steroid oral paste/ointment
- Local Anesthetic ointment
- If ulcer is non-healing, BIOPSY is required.
(iv) Elongated Styloid Process aka Stylagia/ Eagles Syndrome
SYMPTOM-
- Pain may vary from Dull boring to excruciating pain in the throat in the region of the tonsils.
TREATMENT-
- Nerve Block can be given
- Medicines for Neuralgic Pain.
- In refractory cases, STYLOIDECTOMY can be performed.
(v) Glossopharyngeal Neuralgia
SYMPTOM-
- Mild to severe pain pain can occur in areas of tongue, and throat.
The pain can be triggered by:
- Chewing.
- Coughing.
- Laughing.
- Speaking.
- Swallowing.
TREATMENT-
Consult a Neurologist/Neurosurgeon
3. Pain carried to Ear by VAGUS NERVE.
a) Ulcer (Aphthous/ Malignant) over Vallecula, Larynx, Laryngopharynx, etc.
SYMPTOMS-
-SAME AS DESCRIBED IN ULCERS ABOVE
TREATMENT-
- If ulcer is suspected to be malignant, BIOPSY should be done first.
- If ulcer is suspected to be aphthous, Steroid ointment and Local Anesthetic ointment can be applied.
(CLICK HERE TO READ ABOUT THYROIDITIS IN DETAIL)
SYMPTOMS-
- Pain in throat.
- Painful swallowing
- Fever
- Deranged Thyroid function tests
TREATMENT-
- Oral Proton Pump Inhibitor
- Oral Low dose Steroid
- In few cases, Oral Antibiotics may be required.
- Thyroid medicines to correct the thyroid hormone status (if found deranged on report)
- Oral Paracetamol, for pain.
4. Pain carried to Ear by C2, C3 Spinal Nerves
– Cervical arthritis
– Cervical Spondylosis/ Spondylitis
– Caries Spine
SYMPTOMS-
- Neck pain
- Restricted neck movements
- Pain may radiate to head, shoulder, or ear.
TREATMENT-
Consult an ORTHOPAEDICIAN with a specialty in SPINE/ NEUROSURGEON.
5. Pain carried to Ear by FACIAL NERVE.
(a) Geniculate Neuralgia
TREATMENT-
Consult a Neurologist/Neurosurgeon
(b) Bells Palsy or FACIAL NERVE PALSY
(CLICK HERE TO READ ABOUT BELLS PALSY IN DETAIL)
TREATMENT-
- Reassurance.
- Analgesics: For the relief of ear pain.
- Eye Care: Eye must be protected against exposure keratitis.
The preventive measures include–
a. Artificial tears (methylcellulose drops) every 1–2 hours and 4–5 times per day.
b. Eye ointment followed by patching or taping the eye.
c. Cover for the eye in night.
d. Protect the eye from wind, foreign bodies and drying with glasses and moisture chambers.
e. Temporary tarsorrhaphy may be needed in some cases. - Physiotherapy: Active facial movements should be encouraged.
- Steroids
(c) Herpes Zoster Oticus aka RAMSAY HUNT SYNDROME
TREATMENT-
- Tab. Acyclovir 800 mg 5 times a day or Famcyclovir 500 mg tds or Valacyclovir 1 gm tds for 7 days.
- Tab. Prednisone tapering dose 6 days course beginning usually with 1 mg/kg.
- Topical antibiotic/steroid ear drops.
- Eye care as advised in BELL’s PALSY.
5. Psychogenic
Sometimes ear pain can be associated with mental illness.
TREATMENT-
Consult a PSYCHIATRIST.
THANK YOU
WATCH INTERESTING ENT-related VIDEOS ON MY YouTube CHANNEL…..Dr. Sharad ENT Videos
MEDICAL ADVICE DISCLAIMER:
This blog including information, content, references, and opinions is for informational purposes only.
The Author does not provide any medical advice on this platform.
Viewing, accessing, or reading this blog does not establish any doctor-patient relationship.
The information provided in this blog does not replace the services and opinions of a qualified medical professional who examines you and then prescribes medicines.
And if you have any questions of medical nature, please refer to your doctor or the qualified medical personnel for evaluation and management at a clinic/hospital near you.
The content provided in this blog represents the Author’s own interpretation of research articles.
